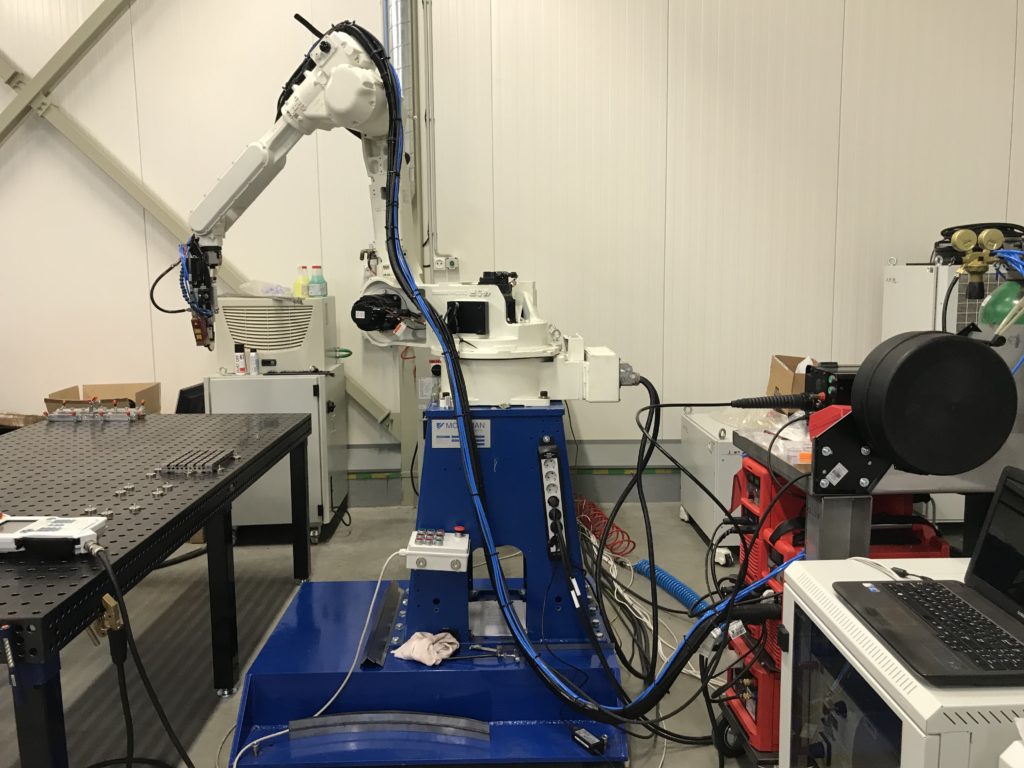
PAW – Plasma arc welding. Plasma welding is an intermediate welding method between the TIG welding and the laser welding.
This welding method features a more concentrated directional electric arc, than that of the TIG method, which is significantly narrowed by the cooled gas tip – nozzle, which directs the plasma gas flow towards the welded piece.
The arc is narrower and more concentrated, therefore this method is not as sensitive (to the increased gap between the tip and the piece), as the TIG.
The seams obtained during the plasma welding are thinner, as the heated surface area is smaller, therefore the products experience less deformation caused by high temperatures.
Compared with the TIG method, the plasma welding features 20-25 % faster welding speed.
As the welding tip has no protruding electrode (as in the TIG method), the welding trajectory is difficult to design and program, as there is no applicable guiding mark.
The above mentioned difficulties may be solved by the following:
Mounting an additional optic automatic welding seam tracking system; however this system is often more expensive than the robot welding system itself, and it often has deficiencies;
Re-adjusting operating position of the electrode by protruding the electrode from the tip, e.g. 2 mm; in this case, the tip of electrode acts as a guiding mark for programming the trajectory. Upon completion of adjustment, calibration and programming of the trajectory, the electrode may be adjusted to the operating position; afterwards, pilot arc may be activated and welding initiated.
In case of stainless steel welding, argon or argon and hydrogen mixture is usually used as the plasma gas. Argon gas or argon-helium mixture is often used for welding non-ferrous metals.
Please contact us, if you are interested in this type of welding system:
